Master-Follower feature
This feature has been implemented to help companies to manage a big set of requirements and certifications by allowing users to create a “Master-Follower” copy of requirements. In this context, users can keep the Master copy of all requirements in a single project and Follower copies on projects where these requirements are applicable. With that setup, if a change needs to be made on all copies, the modification can be done once in the Master copy, and the changes can be propagated to the Followers.
Change propagation is unidirectional, i.e., it can be from Master to follower and not vice versa. The attributes that can be currently and copied are detailed in the Reuse Requirements page.
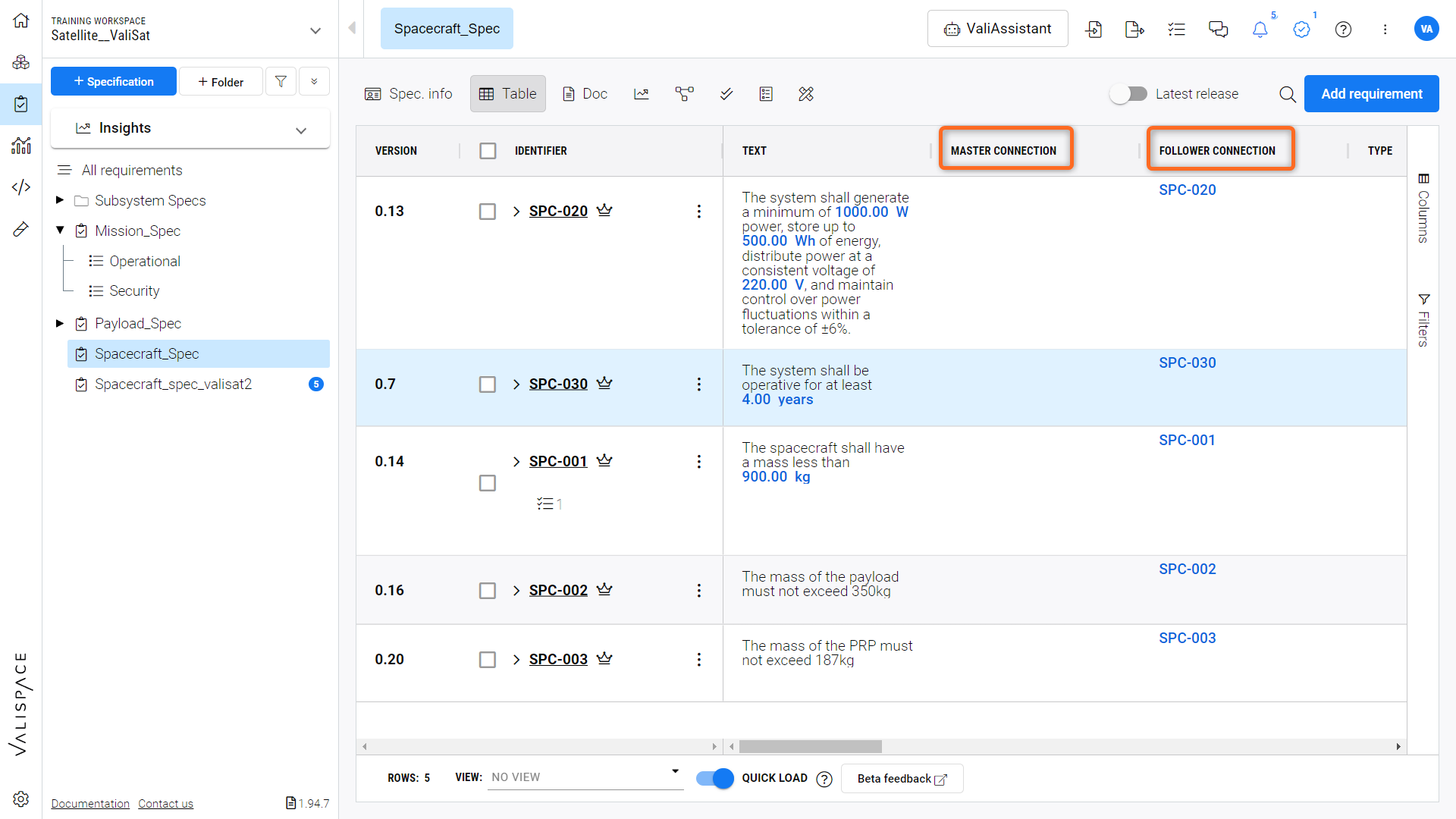
Master and Follower Connections - Columns indicating the Master follower connections between requirements
When you create a Master requirement, the crown icon shown below will be displayed by the side of the requirement identifier.

When the Follower requirement is up-to-date with the Master requirement, it will display this green icon:

If some change in the Master requirement still needs to be approved and propagated, the following icon will be shown:
The blue pencil icon will appear when a change in the Master requirement was rejected (therefore not propagated) or when a change was made directly to the Follower requirement.

If the chance in master requirement is rejected, the icon will be shown within the details sections> Master/Follower
Creating Master-Follower Copy
In this use case, we are copying the payload’s requirements of a satellite Valisat to another satellite Valisat_2 as both are designed for the same mission objective and are using the same payload ‘Synthetic Aperture Radar’- SAR to achieve it. To create a Master-Follower connection, select the set of requirements to be copied. In the action column (1), you can find the Reuse icon (2), click it, and select “Master-Follower Copy”(3) (refer to the Figure Master-Follower Copy).
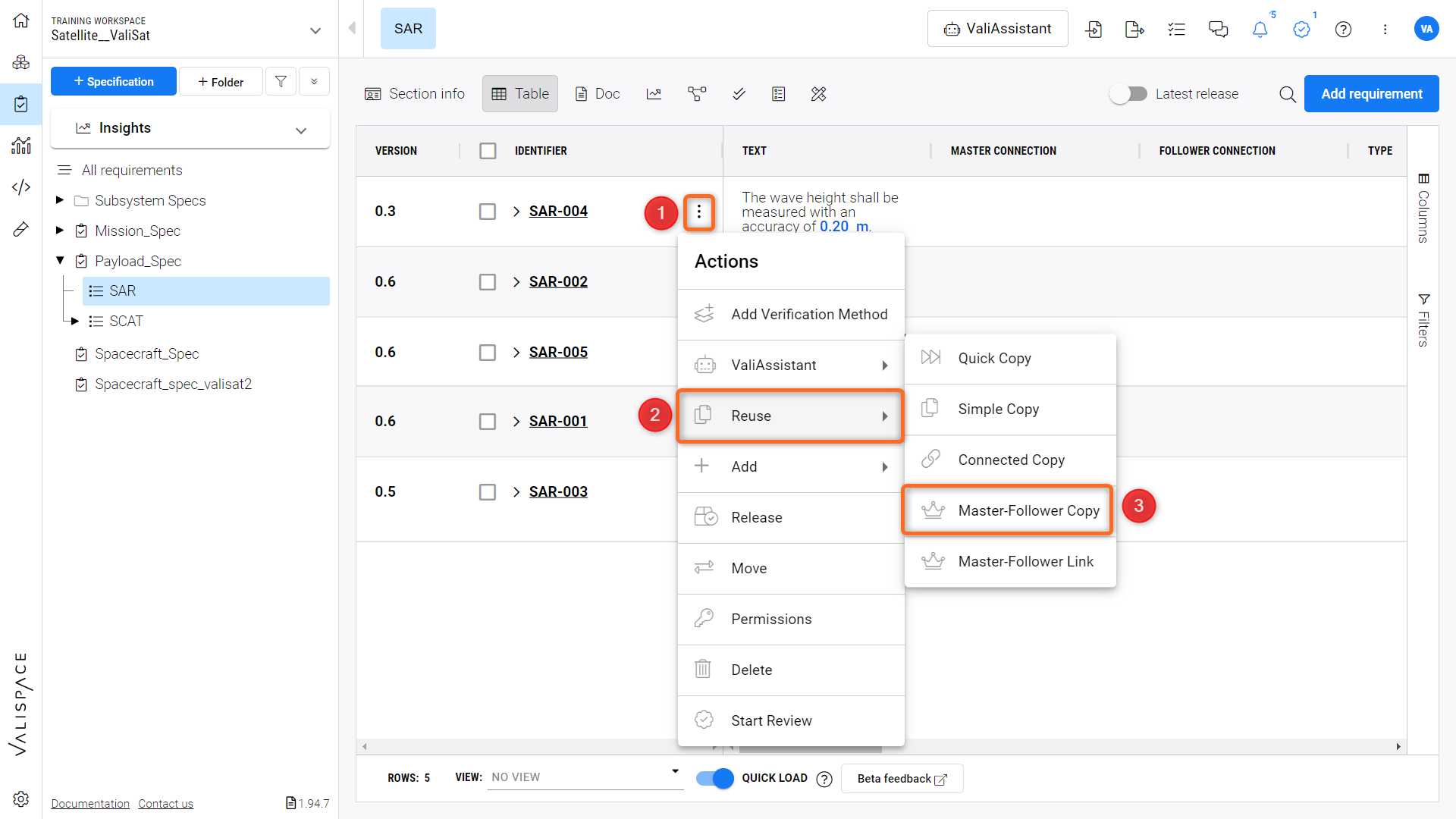
Master-Follower Copy - Illustration of the process to create a Master-Follower copy.
The Reuse Wizard appears, with the ‘Master-Follower Copy’ type of copy selected. Next, the destination of the follower can be selected. Once the destination is set, the user can review the requirements to be copied and their identifier. Next comes the selection of which fields should be copied and synced. Finally, click “Create Copy” to finalize the creation of the follower.
The video below gives an illustration of the process.
Master-Follower Copy video - Illustration of the process to create a Master-Follower copy
Further details on the Copy Wizard can be found in → Reuse Requirements page
Acceptance of Follower requirement
Once the creation of the Master-Follower is concluded, the follower requirement will be available at the selected destination but in a “read-only” mode.
To enable the follower requirement for editing, it’s required to perform a “Follower Entrance Review” in the destination (Specification or Section). That can be done for a single follower or to a group of requirements as shown in the figure Follower Entrance Review below.
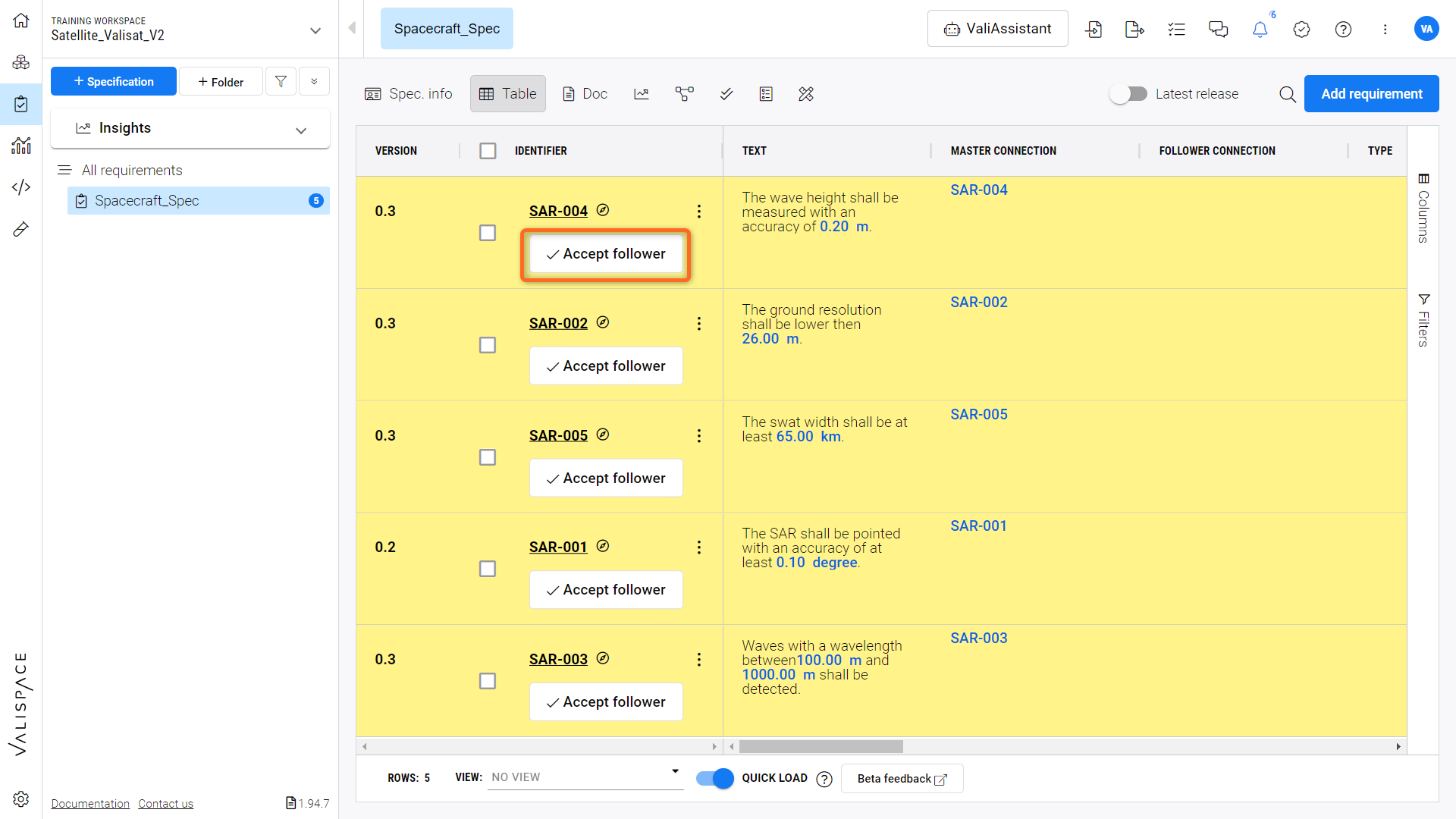
Follower Entrance Review - Visual representation of the "Follower Entrance Review" for accepting the Master follower connection.
You can accept the followers individually or in bulk by following the steps in the video below.
Change in the requirement
Furthermore, if there is any change in the data of the master requirement, the change can be propagated to the follower. The follower will be notified of the change, and the user can decide if the change has to be accepted or ignored manually. When there is a change in the ‘Master’ requirement, the follower requirement ‘Propagation changes’ icon (1) appears in the Action column of the particular requirement.
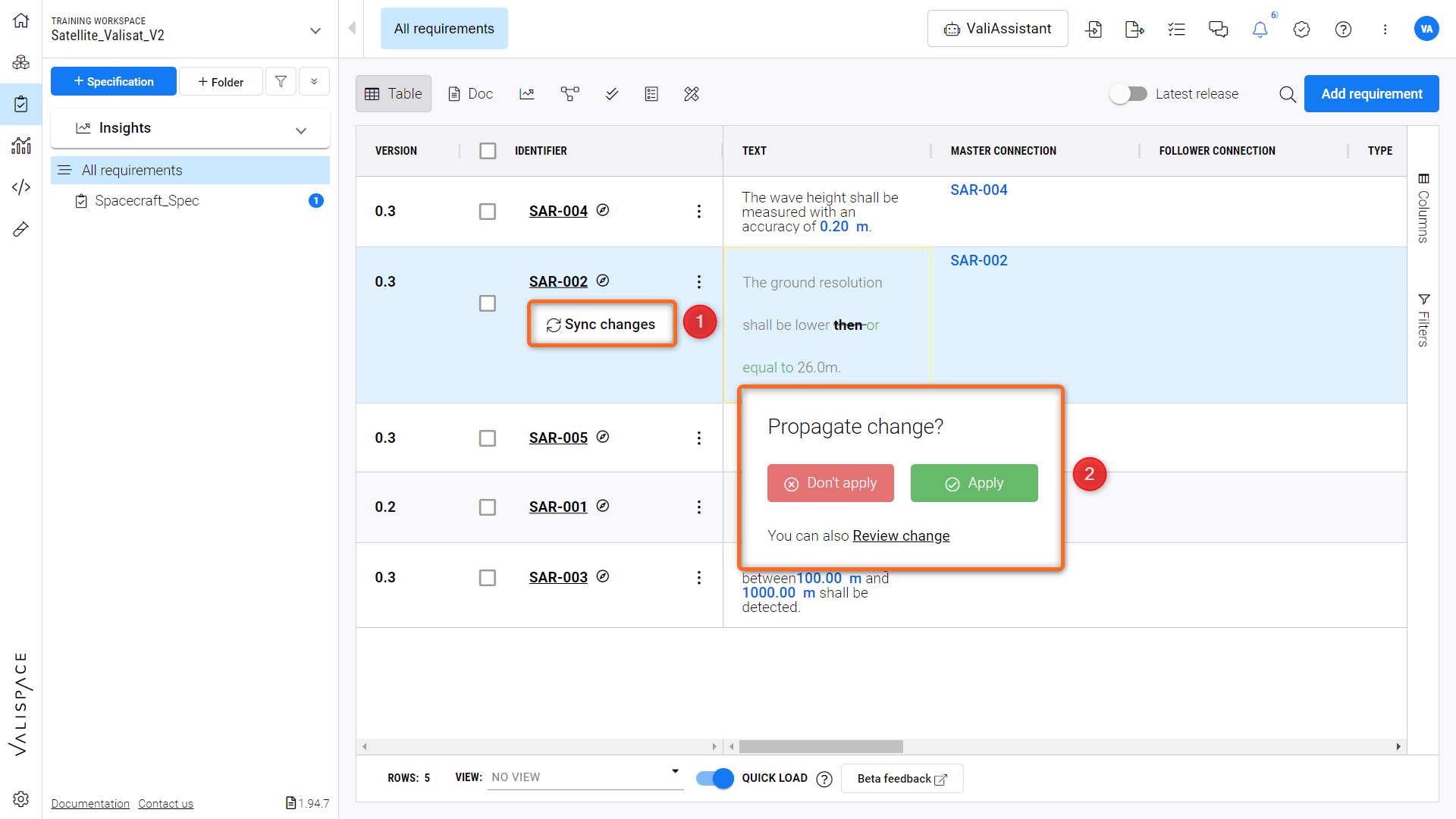
Change Propagation Notification - Demonstration of notifying and applying changes from Master to Follower requirements.
Also, the modified requirement will have a yellow box to highlight the change. When you hover over the box, a pop-up appears (2) where the user can also choose to propagate the changes. Refer Figure Change Propagation Notification .
Only the owners of the requirement will be able to propagate the changes through “Apply” or “Dont Apply”. If a owner is not specified to the requirement, the users with “Read & Write” access will be able to apply or reject the propagation.
Apart from the owners, the users with admin rights and manage level permissions can propagate these changes from Master to Follower.
Clicking on the propagation change icon, a popup appears in which you can either apply, don’t apply, or edit the change implemented in the Master. The user can select the required action accordingly and save it (refer to the Figure Change Propagation dialog box).
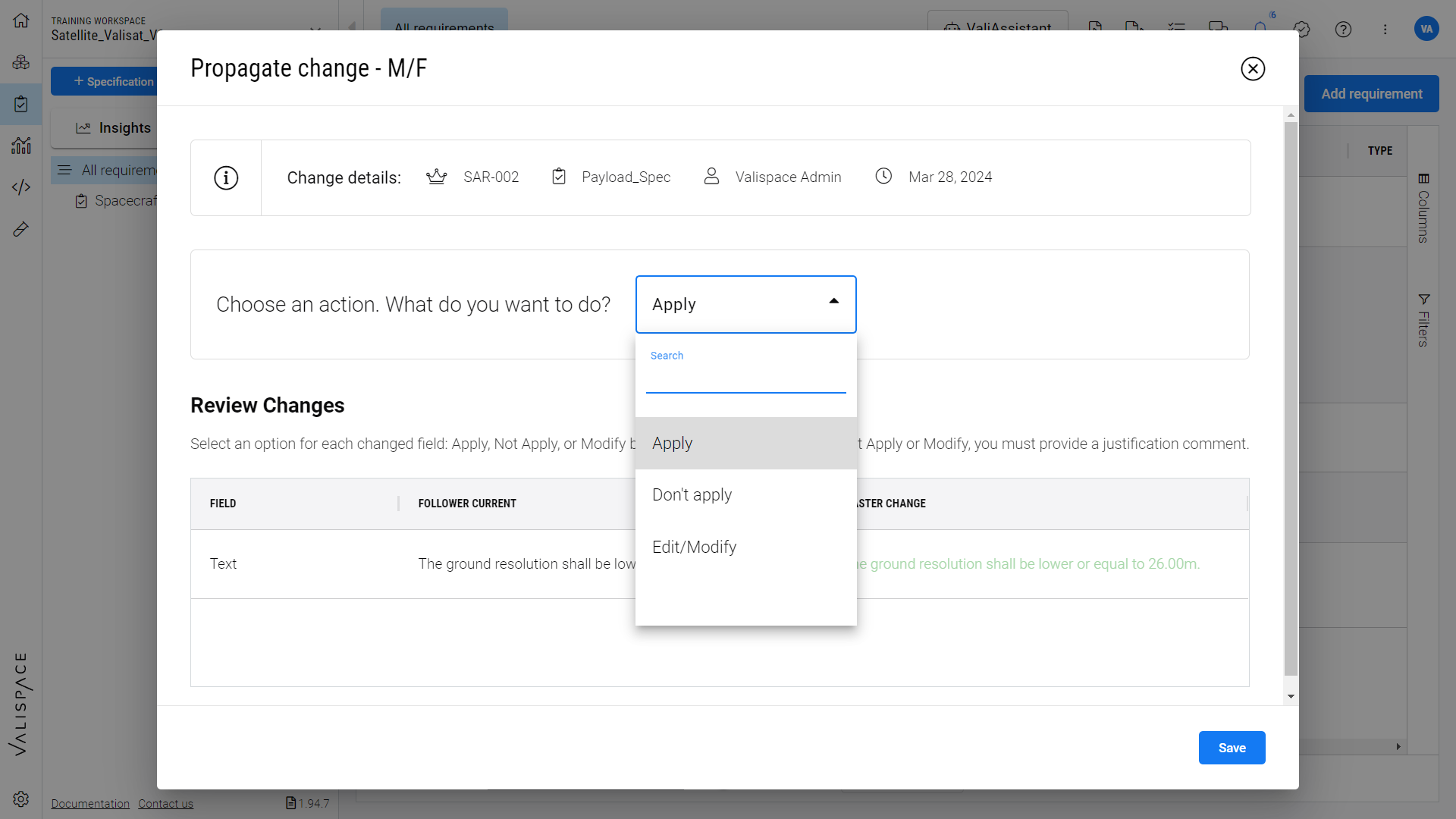
Change Propagation dialogue box - Detailed process of selecting actions for changes propagated from Master to Follower.
The video below displays the complete process:
“Disconnect” feature
Rather than discarding a connection completely and losing its link to the master, the user can select the disconnect option . It will disconnect the follower from its master but will allow the user to reconnect it later if needed. This option can be found by clicking on the three dots (1) in the requirement’s row and towering over the “Connections” (2) option and then selecting the “Disconnect” option (3) (Refer to the Figure Disconnect Feature Illustration)
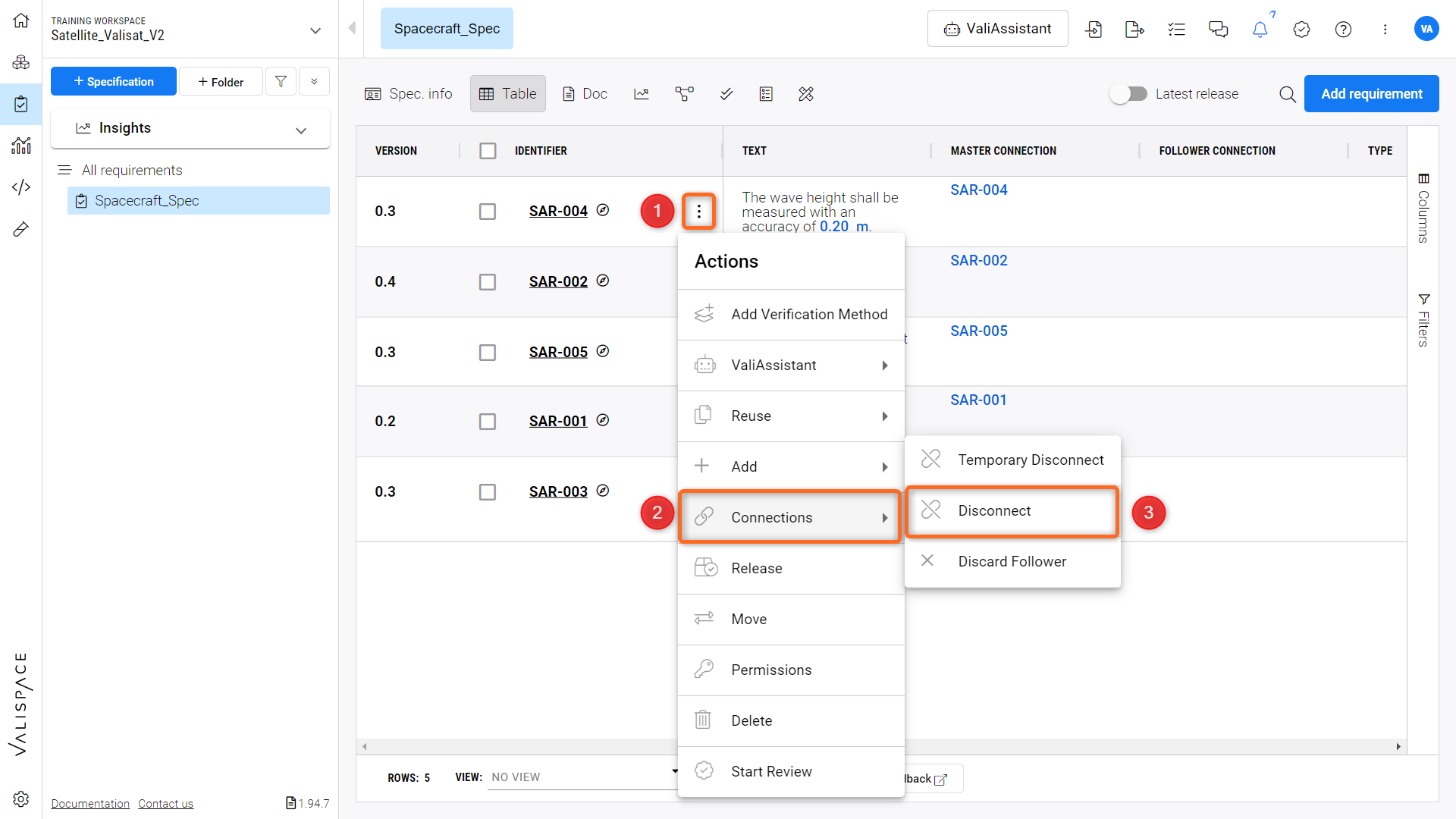
Disconnect Feature Illustration - Visual guide to using the "Disconnect" feature to sever the Master-Follower link temporarily
The discard option lets you permanently remove the master follower connection while the temporary disconnect lets you disconnect temporarily and can be reconnected/resync after certain period of time refer Figure Resync
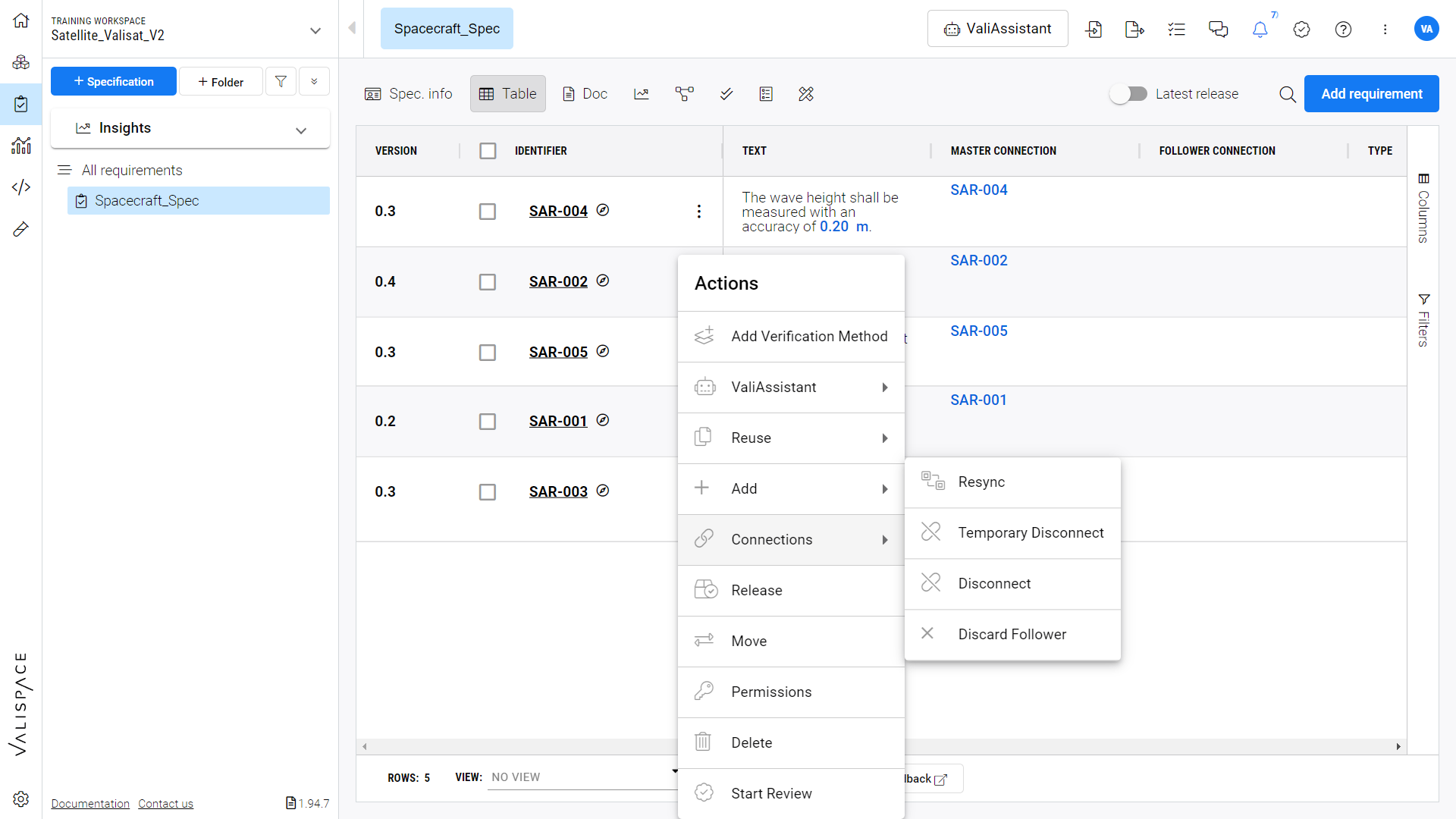
Resync option - Option to resync the disconnect or discarded follower
Changing the Synced fields
After a Master-Follower connection is established, the synced fields can be changed at any point in time, either for a specific follower or for all the followers of a Master requirement.
That is done within the Requirements(1) “Master/Follower” (2) section via the Action(3) “Change Synced Fields”(4).
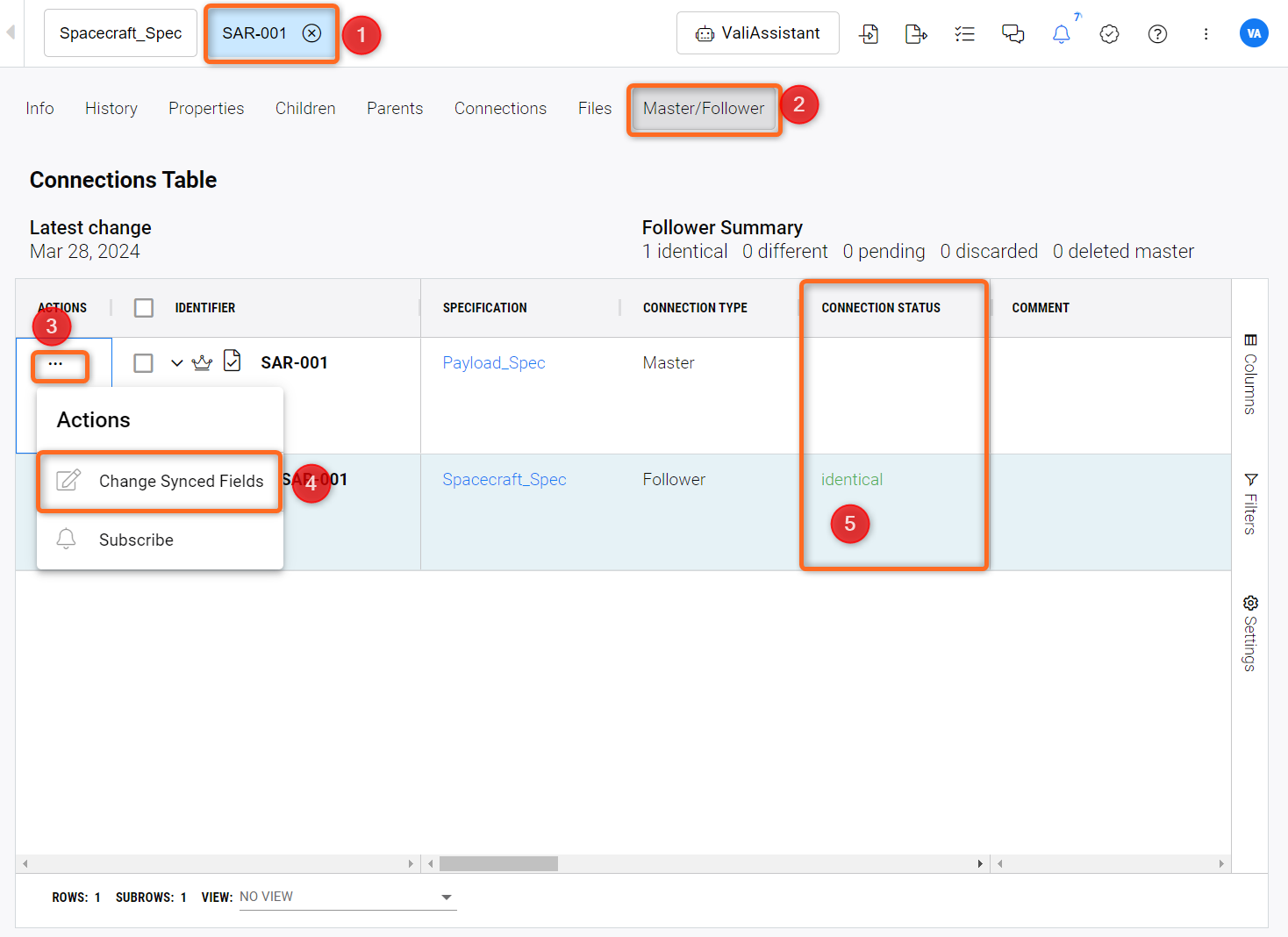
Synced Fields Modification - Explanation of changing synced fields in a Master-Follower connection.
This section also shows the connection status(5) between the master and follower
If the Action is triggered from the Master Requirement, the Changes made to the Fields Synchronization will apply to all the followers of that Master.
If the “Change Synced Fields” is triggered for a specific follower, only those followers synced fields will be changed.
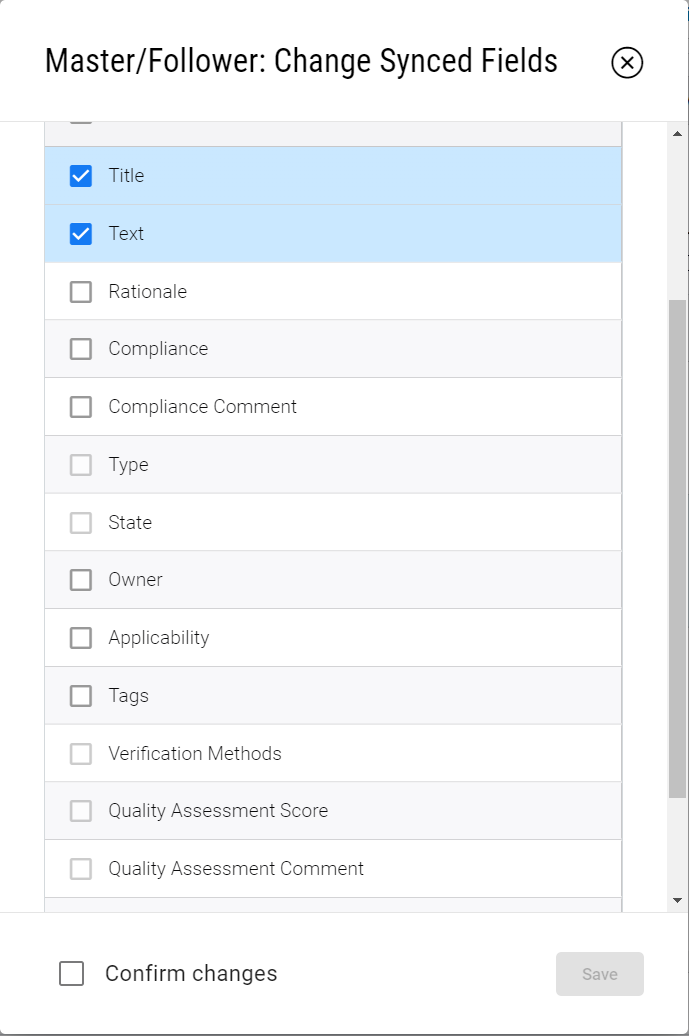
Change Synced Fields - Available fields
Creating Master-Follower Link
Another way to connect requirements with a Master-Follower relationship is by the “Master-Follower Link”. This allows the user to create this type of relationship between objects that already exist in the Requirements and Systems Portal without the need to generate new copies.
To do so, the user should select which requirement he wants to be the Master and then select the option “Master-Follower Link” in the Reuse icon.
There, the user can select which requirements should be considered as followers for the selected Master.
Once the process is complete the user still needs to confirm the follower entrance
The video below shows and example if this process.
Master follower requirements representation in Connections graph
Now, the user can see the Master-Follower connections in the connections graph of the requirements module. Each colored connection shows the state of the Master-Follower relations (1). Refer to the Figure Connections Graph Representation.
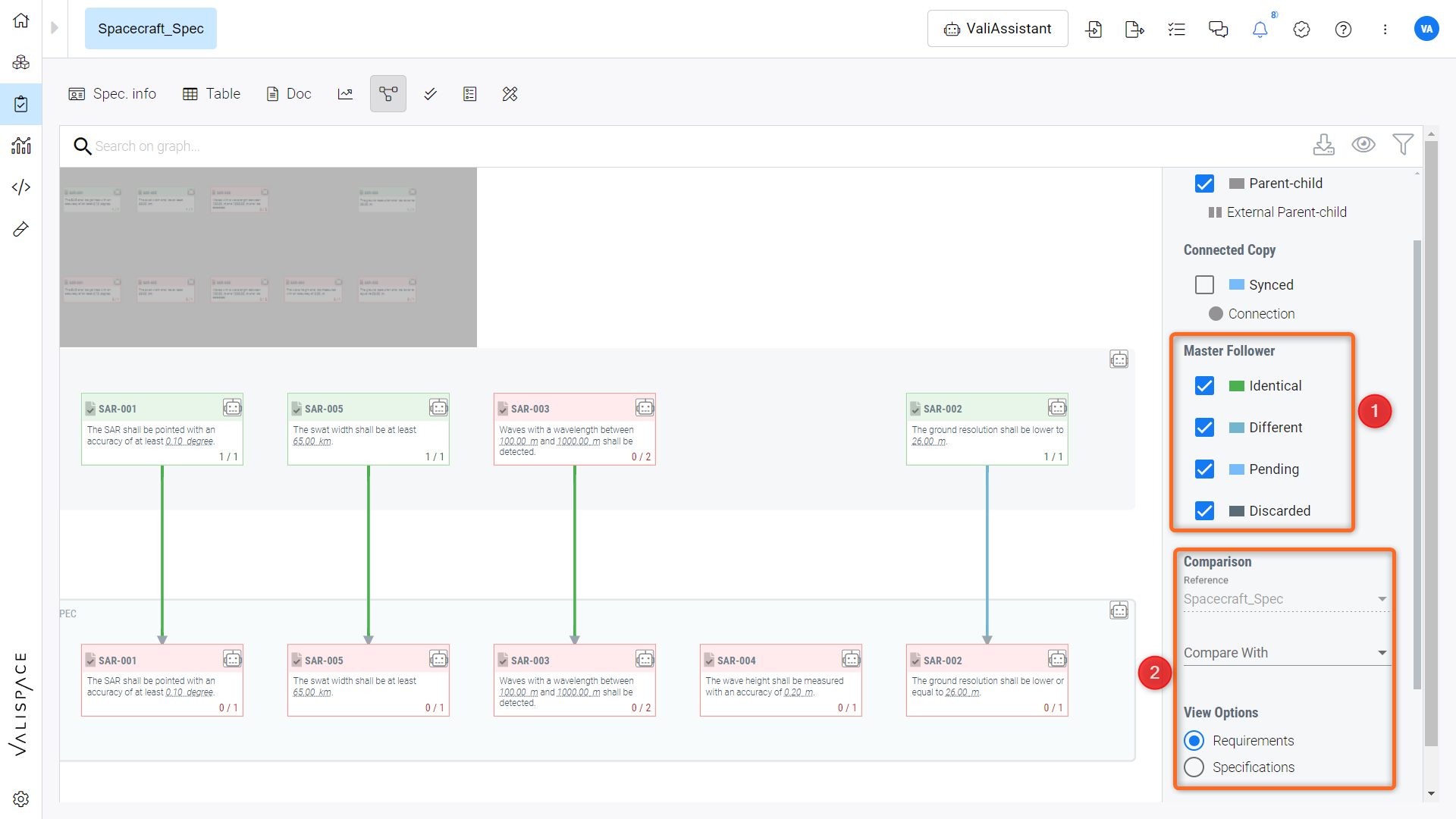
Connections Graph Representation - Display of Master-Follower connections in the requirements module's connections graph.
For example, the green connections show that the Master-Follower is the same, while the yellow ones show that changes haven't been propagated by the owner of the requirements. If the connections are blue, that means the changes made in the Master were not applied to the Follower while the grey ones show that the Follower requirement is discarded/disconnected.
Apart from the coloured connections, the user can now compare two different sets of specifications, which can be within the same project or different projects. The main application of this feature is to compare the Master/Follower specifications or requirements. The comparison tool (2) is within the connections graph.
Use Cases
This feature is helpful when various blocks have similar requirements and need not be added manually every time. The following example can be referred to for better understanding:
Case 1: Satellite subsystems
We have twin 3U satellites with slightly different imaging devices as their payload.
Consider twin 3U satellites with the same design and mission objective except for their propulsion system. While the Vali_Cubesat_1A satellite has a cold gas thruster, the Vali_Cubesat_1B uses ion thrusters. Hence, the requirement changes only for the propulsion system, and all other requirements can be defined for Vali_Cubesat_1A and then copied to Vali_Cubesat_1B.
Case 2: Wing anti-ice system requirements (ATA 30-11)
Let's consider you are the systems engineer for compiling the list of system requirements for the Wing anti-ice system for an aircraft. The company manufactures multiple models and all the models might have the same set of requirements for the wing anti-ice system. Instead of creating the same set of requirements/ specifications, the user can do the Master-Follower copy and to all the other model projects. Whenever there are changes in the system design, the system engineer can allow/disallow the propagation to other projects.
.png)